SNEC E-magazine
"Start-up India" Developing Entrepreneurship for Sustainable Employment
Dr. Umasankar Saha Dept. of Commerce

Introduction
The economic growth and sustainable economic development depends on productive and creative human resource. Larger the number of creative human resource better is the economy. Creating effective entrepreneurship in various need-based innovative productions vindicate sustainable economic development which ensures high value addition and value creation by means of generation of employment of economic resources. Greater the purchasing power in the hands of greater number of people better is the health of the economy. Start-up ventures are dependent on innovation, science and technology, effective human resource management. During human progress, science is evolved out of its corresponding art (Herbert Spencer). The Indian government under the leadership of Mr. Narendra Modi has realized the people of India have enormous potential to be creative entrepreneurs with promising start-ups. Many bright students coming forward for starting up their own business, but owing to financial contraints and other issues, they are unable to do their creative enterprising activities through start-up ventures. Therefore, Government of India has decided to open a website www.business.gov.in to offer gift as a nation wise program- “Start-up India”. Keeping in mind the objectives of the start-up India measures as well as financial packages in terms of scholarship grants for the meritorious students in India have yet to be made adequately available having action orientation through the budgetary numbers. The budgetary allocatios for research and development in core fields of science are still found to be inadequate although we have received freedom over seventy years. It is observed that a meagre six per cent of GDP (gross domestic product) is granted as optimum budgetary number for higher education in India.
“Start-up India” is a revolutionary scheme. Creative entrepreneurs have ideas and capability,
the government will give them support to make sure they can implement their ideas and grow.
Success of the scheme will eventually make India, a better economy and a strong nation. The
Prime Minister of India, Shri Narendra Modi had announced the “Start-up India” initiative this
year in his Independence Day speech. The Prime Minister of India, Shri Narendra Modi had
announced the “Start-up India” initiative this year in his Independence Day speech. This
initiative aims at fostering entrepreneurship and promoting innovation by creating an ecosystem.
This paper has been organized into five sections: section-I: aims of the Start-up India Plan;
section-II: for start-up India -the action plan: section-III: Opportunities and challenges; section-
IV: Towards Effective financing of Venture Capital; section-V: Concluding suggestions.
Key words: innovation; Start-up; venture capital, bootstrapped, angel investors.
Section-I: Aims of the Start-up India Plan
The aim is that India must become a nation of job creators instead of being a nation of job seekers. The Prime Minister of India would formally launch the initiative on January 16, 2016 from Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi. A significant number of young Indian entrepreneurs (over 2000) have embarked on the journey of entrepreneurship through Start-ups. As a key component of this “Start-up India launch, Government of India was organizing a global workshop on “Innovation and Start-ups on January 16, 2016. Shri Narendra Modi, Prime Minister of India was the Chief Guest on the occasion. This workshop aimed to provide a platform to bring together all stakeholders, stimulate dialogue on key challenges that the Indian innovation ecosystem currently faces, and provide the potential solutions to address them. Fostering a fruitful culture of innovation in the country is a long and important journey. Innovation opens up new vistas of knowledge. Today’s knowledge economy is based on the brain-capital based entrepreneurs. Knowledge economy makes everyday life more prosperous, happy and healthy by achieving sustainable economic development. This needs care of juvenile young Indian scientists and knowledge-based entrepreneurs in every field of studies and every facet of life. The Ministry of Science and Technology as well as the Ministry of Human Resource Development in India must go hand in hand. The Department of Science and Technology (DST) is the nodal authority to promote science and technology activities on every facet of everyday life. DST has set up National Innovation Foundation (NIF) of India which has set a goal of providing institutional support in scouting, spawning, sustaining and scaling up grassroots green innovations and extending all helps to self-supporting activities. Startup India is a flagship initiative of the Government of India, intended to build a strong eco- system for nurturing innovation and Startups in the country that will drive sustainable economic growth and generate large scale employment opportunities. DST is attempting to harness advancement in science and technology for the benefit of all humankind. In order to meet the objectives of the initiative, Government of India is announcing this Action Plan that addresses all aspects of the Startup ecosystem.
Section-II: For Start-up India - The Action Plan
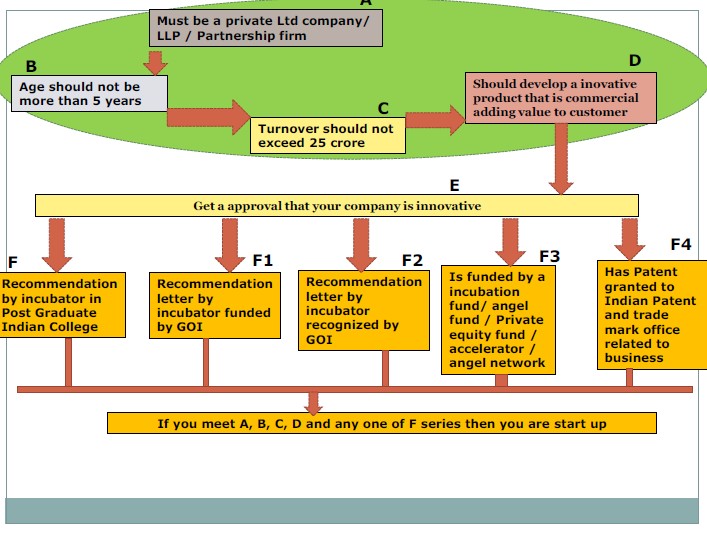
Many entrepreneurs were excited by the announcements made by Prime Minister Narendra Modi as part of the Startup India Action Plan. One of the eligibility criteria states that “The product or service should be a new one or a significantly improved version of existing services or products.” Let’s take the example of startups who are engaged in creating and developing online marketplaces like Flip kart and Amazon. So a new startup engaged in the same field may not be eligible unless its product is significantly improved than what existing players provide. Another eligibility criteria states that the startup should get a recommendation letter from the recognized incubator cell or be recognized by the Government of India (GoI) or should be funded by recognized funds. Now this will be quite a task for startups. Start-up India from job seekers to job creators: Mr. Narendra Modi said that the India Government has been trying to make youths from job seekers to job creators having innovative ideas for launching start-ups. Initially the entrepreneurs will not run after to create money but to devote on their enterprising activities in order to create strong marketing base through customization process of products and services. Here is a quick analysis of the eligibility criteria (please note that the following flow chart is specifically applicable for startups seeking tax exemption):
In this connection, we must remember the effects of disruptive technologies and creative entrepreneurship. Innovative technologies or business models can profoundly affect the functioning of existing industries. The most visible examples are internet-based "sharing services" that are disrupting conventional banking services, flight and railway tickets booking, catering booking, taxi and hotel markets, but there are many others in diverse areas such as finance, retail electricity and automobiles. These disruptive innovations can deliver important benefits to consumers, in terms of new and better services, and can stimulate innovation and price competition from established providers. However, they can also give rise to legitimate public policy concerns (e.g. safety, privacy) and create demands for regulation. Established providers will often lobby for existing regulations to be applied to new providers to lessen their competitive advantage, sometimes claiming rightly or wrongly that this advantage arises from an ‘unfair’ exclusion from regulatory rules.
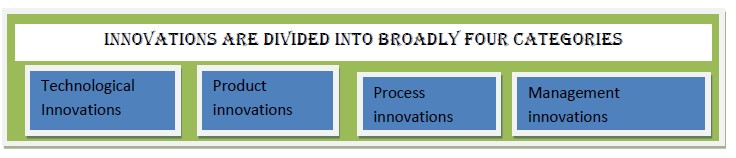
Technological Innovations connote any innovation due to an industrial application of scientific knowledge. These innovations are essential associated with the use of technological knowledge, research and development activities with in-house creativities.
Product innovations connote introduction of new goods and services which are notably improved in terms of design excellence, core characteristics and in-house developments.
Process innovations connote introduction of significantly improved production process comprising of new techniques of producing of goods and services that minimizes cost per unit and maximizes speed, service, quality, simplicity and waste reduction.
Management innovations connote new management practices, innovative ways of doing things and significantly transforming and improving the effectiveness of management functions and dramatic departure from traditional ways of doing activities.
Successful innovations happen when value chain from the lowest levels to highest levels is achieved in a systematic enterprise through the technological innovations with effective implementation of management innovations. Innovations act as driver of economic growth and sustainable economic development. Profitability and success of an organization entails human resource, leadership, creativity, process and organizational culture. Innovation brings about all round impact on the creative entrepreneurship.
Disruptive vs. Incremental:
The term “disruptive innovation” was coined by Clayton M. Christensen, professor at Harvard Business School. In his book The Innovator’s Dilemma, Christensen defines disruptive innovation as products/services that “bring to a market a very different value proposition than had been available previously. Generally, disruptive technologies underperform established products in mainstream markets. But they have other features that a few fringe (and generally new) customers value.” In other words, disruptive innovations will open up a new segment in the market, which early adopters jump on first to be followed by the general consumer audience. Schumpeter mentioned the concept of disruptive technologies in the theory of economic development.
On the other hand, incremental innovations are, according to the Business Dictionary, “a series of small improvements to an existing product or product line that usually helps maintain or improve its competitive position over time.” As opposed to disruptive innovations, incremental ones are more evolutionary in nature, as they won’t allow you to carve out a new market, but instead strengthen your position in the market by simply refining your already existing offering, or offer a product with a slight twist on something that was already successful, and make it your own.
Do People Really Need Innovation?
Back to Apple example, when the original iPad was first launched, people thought, “that’s just a big iPhone,” or, “Why would I need this, when I already have a laptop?” and a half years and nearly a hundred million units sold later, doubters can put their doubts to rest: people actually did have a need for a lightweight device they’d be able to carry around, just to browse the Internet or read books/magazines on. What Apple was able to do was to create a need, find a niche in a market over-saturated with desktop and laptop computers, by simply tweaking their iPhone concept and giving it a larger screen-size. Start-ups that create a need of users of the products and services are obviously able to create value through competitive advantages.
In the Twentieth Century, we had mobile phones and in the Twenty First Century we are almost all having android smart phone in hand. The old mobile phones are now back dated. The old fashioned typewriting machines are not being used only because of the fact of desktop or laptop in hand. So, we feel the innovations are changing our life style. Every innovation gives a boost in the economy.
Let us say you are a burgeoning entrepreneur, or already in the process of creating your own small business with innovative ideas. Your fear is that a product/service you are ready to launch is not innovative enough, that you would not be able to differentiate yourself from the competitive others. What will determine the success of your business is how you manage it, from concept to launch, whether the market has a need for it, and then selling the heck out of it. When trying to raise capital to fund your business, investors and VC’s (Venture Capitalists) will be looking at your business plan, and how you plan on sustaining growth for your company, not just at how “innovative” your product/service is. Venture capitalists are interested to invest into those start-ups (bootstrapped) that have enormous potentialities in creating values in the unexplored markets. In the implementation of the start-up plan the action plan is briefed hereunder.

Creative entrepreneurship business plans can be achieved through the Make India Plan and which can be implemented in the following industries:-
What is 'Bootstrap'?
Bootstrap is a situation in which an entrepreneur starts a company with little capital. An individual is said to be boot strapping when he or she attempts to found and build a company from personal finances or from the operating revenues of the new company.
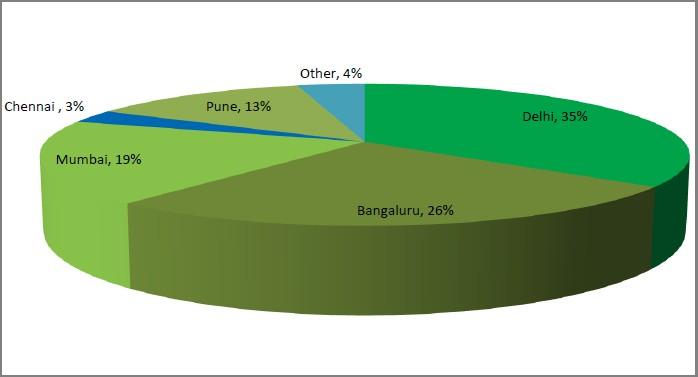
Compared to using venture capital, boot strapping can be beneficial, as the entrepreneur is able to maintain control over all decisions. On the downside, however, this form of financing may place unnecessary financial risk on the entrepreneur. Furthermore, boot strapping may not provide enough investment for the company to become successful at a reasonable rate. The (boot-strapped) start-up hubs in India are significantly concentrated by 79% in three major cities owing to some obvious reasons as shown below.
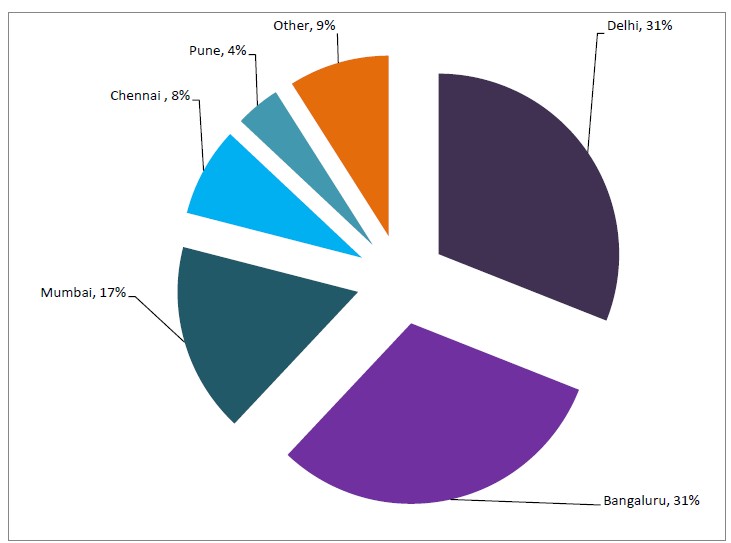
City wise most popular Start-up Hubs in India (Boot-Strapped)
This concentration in Delhi, Bangaluru, and Mumbai is owing to the fact that
1. a sound infrastructure is covered;
2. the best transportation frameworks as well as networks are built up;
3. the political disturbances are minimized at optimum level;
4. business friendly management and work culture is grown up;
5. easy access to policy oriented organizations;
6. sound money market and capital markets networks are operating at sound footing;
7. local self-government is most friendly with business investors;
8. Tax friendly system is being operated;
9. angel investors are mostly available for making investments;
10. Venture capitalists are observed.
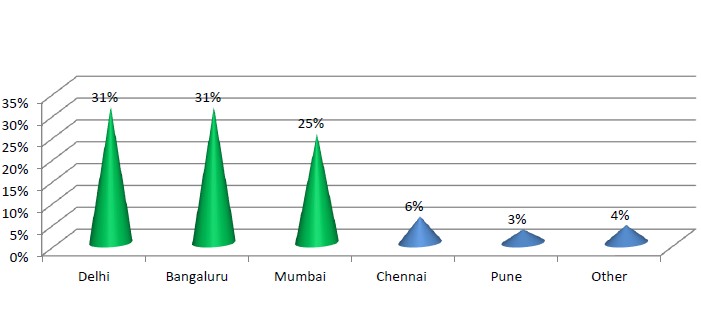
City wise most popular Angel-funded Hubs in India (Boot-Strapped)
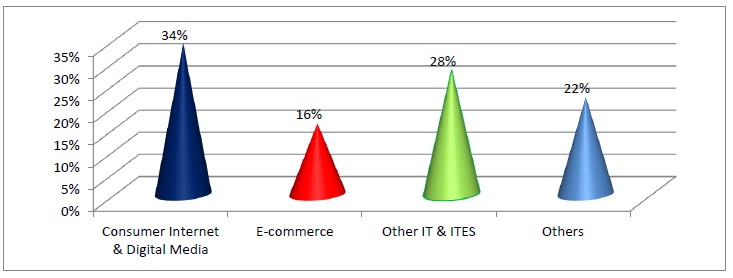
City wise most popular Venture Capital-funded Hubs in India (Boot-Strapped)
Delhi emerges as the most sought after city for starting up because of the under mentioned
reasons:-
1. Developed and industry-friendly infrastructure;
2. All modernized system of transport systems;
3. Quickest Possible Administrative services;
4. Industry-friendly Banking systems;
5. Best net work system all over country;
6. Best work culture;
7. Transparent governance;
8. Easy access to policy making bodies;
9. Industry friendly housing system;
10. Easy access to marketing network.
Section-III: Opportunities and Challenges:
Opportunities: India is the vast populous country just having about 130 billion people which is
proud of having unique culture. India has 31 states 0ver 1600 languages more than 2000 ethnic
group. This unique opportunity is availing almost all country in the globe.
Market potentials: Huge and diverse preschool market is expected to reach Rs133 billion by
2015 as compared to Rs 43 billion in 2010.
Market trends: Compelling demand for quality education and the huge pool of juvenile Indian
youth needs huge job market in India. A large percentage of young families 65% below the age
of 35 many international and local providers lack of preschool regulatory. It leads to shape
Indian market future through education for all.
Challenges: Every sphere of life we need guidance to navigate transparent governance.
Surprising high rentals for premises are observed in metropolitan cities in India. Syndicate
raj/mafiaism/tolabaji is being observed in metropolitan cities particularly in Kolkata in West
Bengal and many other important cities in India.
Emerged Challenges: From an organized study report it is observed that the following challenges have emerged in the
era of “Start-up India” Plan.
Is the Indian education system preparing future employees with the skills your business needs?
Globalization has made the globe very tiny. With the advent of science and technology globe is within our
palmtop. We can sense the significant economic impact of globalization as a result of which human
beings have to be tuned with newer requirements for which they require knowledge. Knowledge is
acquired by prospective workforce and deployed workforce by virtue of academic background and
experiences. Today Human Resource Management is guided by strategic common sense & interest for
particular point of view, change in the policy of selection & recruitment programme, induction
programme, training & development policies, system of education. Educare for all is an urgent need of
the hour. Strategic knowledge management is the key to the success of HRM. Most of the corporate
entities which were enjoying protective economic regime felt real threats for their survival since 1990s.
Knowledge resource has become the strategic weapon for gaining competitive advantage in the era of
globalization.
From a global perspective, the economic challenges of the 21st Century for firms differ significantly from
that of the 1980s and that of the 1990s. In recent era the knowledge management, the process of effective
management and connecting knowledge of people and leveraging that knowledge of people, is considered
to be the key characteristic of superior firms and establishing global competitive advantage.
Importance attached to HUMAN RESOURCE in start-ups as well as in existing business entities:
There would be greater demand for humane approach to manpower. Similarly the need of more
capital intensive methods would result in greater productivity of deployed human forces
necessitating greater motivating and greater human resources approach of management. In order
to achieve large scale production with the application of technical and technological
developments have opened up new training needs for the deployed people at work. Effective
human resources development programmes have therefore become the need of the hour.
Keeping in mind keen global competition, at the end part of twentieth century, threats have been aptly
narrated briefly by Arun Bharat Ram, Sr. M. D. of SRF Ltd. He said that around 25-30 per cent Indian
Corporate entities have to close down operations within 2-3 years owing to the effects of emerging
changes taken place in India which has moved from the regulated and protected regime towards more
open and competitive economy. In this changing scenario of Indian economy, only those corporate
entities will survive who have the capacities to sustain and survive competing through human resources
vis-a-vis knowledge capital as well.
Threats generated owing to the effect of liberalization policies adopted by the Government of India can be
met through effecting corresponding changes in the practices of general management including practices
related to the HRM. HRM needs to think in terms of carrying their workers with them. Convincing the
workers of the management's concern for them may, perhaps, go a long way in getting along with them
and ensuring their better performance for their sustainable growth and development. This has naturally
resulted in the present human resources movement.
Only because of widespread industrial unrest, growing trade union influence on work force, strained
worker- management relationship, increasing gulf between management and their people, emergence of
militancy in trade unionism, and the growing conflict in the industrial relations scene have resulted in
workers getting out of gear of the management in many organizations in India. A good sense has started
to prevail upon the mind set of human resource about the emerging necessity of HRM must be acting as a
system of an entity that has started to inculcate at all levels of organization.
Challenges emerged have far reaching impact upon the HRM for start-ups as well as on existing business entities:
Human resource deployed in any organization has super form of function-ability. In the existing business organizations, deployed HR poses numerous challenges before the HRM. So, it is similar for the start-ups. It is imperative to maximize return on investment made for the deployment of HR. It is widely accepted that the deployed HR is human capital not as commodities, so it has to be leveraged optimally in order achieve the goals of the organization by aptly handling the emerging challenges due to globalization, emphasis on knowledge management, newer organization design, emphasis on Kaizen (continuous improvement), Changing Job Profile, Changing Work force Profile, Increasing Role of Women work force, Making HR Activities Ethical, Attitudes Towards Union, Dynamic Management of Human Relations, Concern for Quality Circle Management, Total Quality Management, Awareness of Quality Work Life, emphasis on core competence etc.
Section-IV: Towards Effective Financing of Venture Capital
This research study has tried to identify the principal features of a very important and growing
but not enough explored field. In this final chapter, an attempt has been made to highlight some
of the major observations by way of recapitulation and offer a few suggestions for improvement
in the future. While preparing this chapter, the researcher has drawn heavily on the outcome of
interviews with the senior executives/entrepreneurs associated with the Kolkata-based software
enterprises and the relevant data collected through field survey.
In India, venture capitalists, in general, do not follow the concepts/ideas developed in the US
regarding venture capital financing. In the US, the venture capitalists are usually high risk-takers
while financing ventures of high-tech entrepreneurs. It appears that most of the Indian
entrepreneurs have a different perception of venture capital. Most of them consider that venture
capital is yet another type of special institutional financing available from the venture capital
companies/venture capital funds, most of which are divisions or subsidiaries of the state-owned
financial institutions and commercial banks (Pandey, 1996). The Indian entrepreneurs, by and
large, do not like to share ownership of their ventures with others. They are very often found
much reluctant to expand and to go public, the reason being fear of dilution of ownership and
loss of control in their business. Again, the venture capitalists in India are often very much
selective and set a number of criteria to evaluate a proposed venture.
The researcher, in course of studying, inter alia, these features of venture capital financing in
India, has particularly focused on the Kolkata-based software enterprises and classified them into
three distinct groups.
1. The first group comprises the enterprises backed by institutionalised venture
capital financing/formal venture capitalists’ funds [group-I, i.e., IVCF].
2. The second group comprises the enterprises backed by non-institutionalised
venture capital financing/informal venture capitalists’ funds (angel investors’ fund)
[group-II, i.e., NIVCF].
3. The third group comprises the enterprises backed by individual venture
capital/self-financing [group-III, i.e., IVC].
It has been observed from the field survey that the Kolkata-based software enterprises in IVCF,
NIVCF and IVC groups are 9.68%, 41.94% and 48.38% respectively. Such data are represented
in a bar chart below.
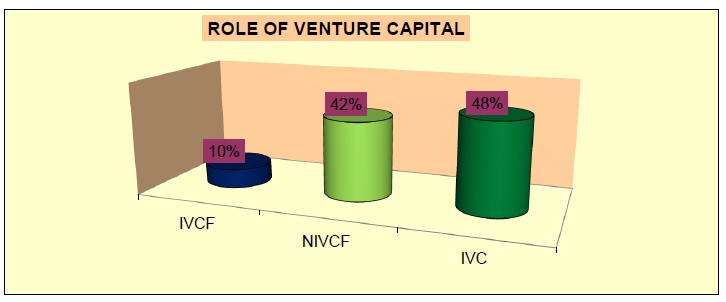
Source: Field Survey Report of Dr. U.S. Saha in his Ph.D. Dissertation
Private equity is the major source of venture capital financing for the development of the
software enterprises in Kolkata. This type of selective form of venture capital financing in a
leading city like Kolkata has largely restricted the development of the hi-tech entrepreneurship,
though Kolkata is otherwise quite rich in terms of availability of hi-tech software entrepreneurs
as well as knowledge workers. The researcher has considered 12 Kolkata-based software
enterprises out of 31 software enterprises in Kolkata (i.e., the effective sample). They have been
classified into the above-mentioned three groups. In the development of the Kolkata-based
software enterprises, the NIVCF and IVC groups have played a significant role when the formal
venture capital financing is too inadequate.
The researcher observes that the Kolkata-based software entrepreneurs within these three groups
have some positive attributes mentioned below similar to the attributes identified by
McClelland [6].
* The software entrepreneurs in Kolkata prefer risky ventures/hi-tech
occupations, particularly in the field of IT-related software development
activities.
* The Kolkata-based software entrepreneurs are moderately high-achievers and
they do not depend on their luck at all. They always prefer to gear up to accept
challenges in the hi-tech sector.
* The software entrepreneurs and knowledge workers in the sector of software
development and IT-related services in Kolkata have already started migrating to other
States on a large scale mainly due to the apathetic attitude on the part of the State policy-
makers.
* The software development process can be divided into two consecutive stages (viz.,
creative stage and non-creative stage) as viewed by most of the respondents in the
Kolkata-based software enterprises at the time of interview.
* The creative stage involves conceiving of ideas and programming that require high
quality knowledge workers. The non-creative stage comprises system
engineering/designing/coding/testing etc. which require lower level of skill.
* The Kolkata-based software knowledge workers are efficient enough to work at the
creative stage as well as the non-creative stage. The creative stage relates to onsite
programming services. Indian software professionals have already proved themselves
worthy being employed as programmers. The Kolkata-based software knowledge
workers are equally efficient in both the stages of software development.
* The Kolkata-based software exporters are focusing their attention on custom computer
programming, manpower planning, consultancy and developing customized software
products.
InnoVen Capital India (formerly SVB India Finance) is the premier provider of “venture debt” to
high growth Indian start-ups backed by top-tier venture capital investors. The Company provides
multiple sources of debt capital including venture debt, acquisition financing, growth capital and
capex financing. InnoVen Capital has received investments from Temasek, an investment
company based in Singapore and United Overseas Bank. InnoVen Capital has also set up
operations in South East Asia.
For more information on InnoVen Capital, please visit www.innovencapital.com and follow
@InnoVenCap_IN For more information on the report, please contact:
InnoVenIndia@innovencapital.com
Section-V: Concluding Suggestions:
Socio-economic-techno-political entrepreneurs are obliged to decide what is appropriate for value-creation vis-à-vis value-addition for the nation at large. They carry out the responsibilities of their own positions and have extraordinary influences on each person with whom they directly/indirectly interact. Values drive our attitudes towards achievement of goals. Values bring satisfaction for stakeholders. Values and Ethics act as an integral part of business. Value is more than profit. In today’s globally competitive landscape entrepreneurs involved in value- adding enterprising activities are inventors, innovators, global supply chain managers and service providers. Entrepreneurial production-centric activities have evolved, but understanding of measurement and disclosure through value-added have not yet turned into high human want satisfactions. So, the need of development of human capital by means of value-adding multiplier (VAM) for the benefits of the nation at large is the order of the day (Saha U.S., 1998). Value- creation vis-à-vis value-addition is the art of the deployed human capital (Saha, U.S., 1998).
Summary of the Empirical Findings
West Bengal, one of the highly industrialized States of the country, has lost its earlier status. Its
share to all-India Net Value-Added (NVA), share of employment and factories has come down
phenomenally. Value-added performance of the manufacturing sector has gone down. The
language of the socio-economic-techno-political entrepreneurs are not at all befitting with the
basic demands of the prospective investors in the state. The state is vastly affected because of the
fact of political turmoil prevailing.
Besides this the researcher has studied respondents’ views based on questionnaires; socio-
economic-techno-political factors have been focused for the development of the manufacturing
enterprises in Kolkata. Most inhibiting factors have been focused under groups based on the
analysis of observed data by non-parametric approach. The inhibiting factors though apparently
hidden are exposed through the study based on non-parametric approach. These inhibiting
factors are studied through the respondents’ views. Human capital development is the ultimate
objective and quality assurance is root mantra. Culture of quality has to be developed in the
manufacturing sector keeping in mind the upcoming global challenges. We need to create our
own brand image in the global market places to earn foreign exchange.
Summary of the Major Suggestions
The investors are really afraid of making investments in employment generating huge
manufacturing industries in West Bengal. Industry-friendly environment is absent as an effect of
political barbs over the decades. Instead of offering impetus to the industrialists and investors,
unscrupulous socio-economic-techno-political entrepreneurs have delivered utterly unfriendly
messages. Start-ups ventures are almost tending towards null in the state because every means of
production system in the state is being unethically controlled by the syndicate raj system which
is not at all legally/officially approved but in the common parlance of socio-economic-techno-
political culture which is not at all praiseworthy. Drastic pragmatic steps against this syndicate
raj are urgently needed to bring back the traditional and historical cultural heritage and industrial
atmosphere in the state. The economic resources along with human resources are not being
adequately employed in the system of economic activities gearing up start-up ventures in the
state.
In the context of land hungry state of affairs Robert M. Solow's [1] model of economic
development and growth by means of deployed skilled human capital and growth of capital
formation in the field of service generating industries, hotel industries, and information
technology-centric service sectors is feasible. In the state of West Bengal value-added economic
growth is sustainable only by means of those industries that are ought to be equipped with
technologies and are simultaneously generating huge employment of human capital vis-à-vis
knowledge capital. Revival of economic status of the state urgently needs those investors who
are equipped with modernized technologies and huge capital so that they can invest their funds in
manufacturing industries in small pieces of land. Large-scale heavy industries being equipped
with technologies and hugely labour intensive are most needed in land hungry overpopulated
state. Industrial investments in some selected states in India have recorded a rise up to December
2012. The report is represented in the Bar Chart as depicted below.
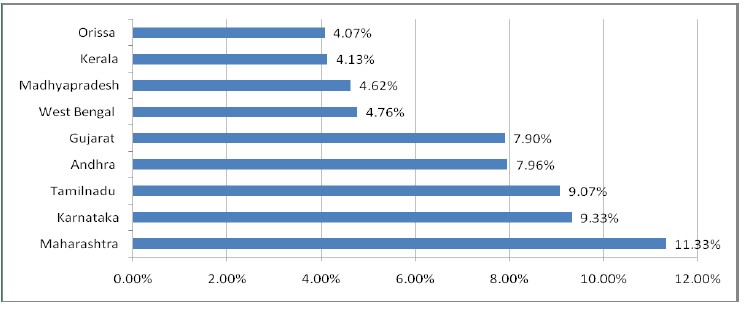
Source: Times of India publication in Bengali Eai Samoy, 18-01-2013.
Until and otherwise the massive investments for scattered industrialization vis-à-vis
urbanization are done in the state, its economy can never be able to sustain own economic
stability in terms of value-added growth. Massive production and value creating culture amongst
the deployed work force is the ultimate solution to the need of crisis of values. In this subject the
researcher has described that the enhanced value-added wealth is the socio-economic-techno-
political performance indicator significant for the stakeholders and society as a whole.
Localized infrastructural development clustering to the city of Kolkata does not bear the huge
pressure of migrated human forces. The process of urbanization needs dispersal of infrastructural
development and creating of big cities all over the state apart from the clustering needs of
Kolkata. Sacrifice of obesities and vices in the mind of the socio-economic-techno-political
entrepreneurs will essentially boost up the process of value-addition in every field of production
and service generating sector as value-added performance is based on ethics in business. Factors
leading to ensuring good governance, stability, sustainable economic development and growth
will accelerate the pace of economic development by means of application of the unified theory
of value-addition [2]. The unified theory of value-addition is the most pragmatic approach of the
researcher because the concept of income [3] or profit has suffered several metamorphoses at the
hands of the economists from the remote past. The value-added concept [4] has particularly been
developed with the perspectives of ascertaining the value-added wealth of the nation. The
application of the unified theory of value-added needs ethics-centric social climate [5] for
innovative entrepreneurs [6] who want to grow contributing a lot for the economy by means of
enormous value-addition which is the ultimate objective of every economy. The largest and
fastest growing democracy on the earth, India has today emerged a major leader to handle its
vast pool of human capital with the intensification of creating value-added wealth in its vast
manufacturing sector. But in the era of “Start-up India” juvenile creative entrepreneurs are really
starved of seed capital financing for their start-ups. The fledgling entrepreneurs are very shy of to
start their start-ups having some fear in their mind sets owing to the major effects of hooliganism
and mafiaism through syndicatization of all factors of production of goods and services.
References
1. Robert M. Solow, A Contribution to The Theory of Economic Growth, Quarterly Journal of Economics, February, 2013, The Solow Growth Model, Robert Solow (1956), T.W. Swan (1956).
2. Unified theory of value-addition is a thematic research work based on empirical studies done by the author by analyzing secondary data as well as respondents’ views under the non-parametric approach. Most significantly, Unified theory of value-addition entails the ideas on value-addition, conceptualization of values and ethics, total quality management, and finally studies based on application of correlation between the value-addition and payments for maintenance of deployed human capital.
3. As the economists are advanced by their own concepts of income, so has the accountants their own attitude towards these concepts developed over the passage of time. The accountants are guided by their own conceptualization of income, though they did not appear to be as acute or radical as those of the economists. The theories of economics have been recognized over the globe in awarding Nobel Prize since 1969. So, the present discussion about the unified theory of value-addition is basically based on the literature of economics.
4. D. Solomons, Economics and Accounting Concept of Income, an essay published in Readings in the Concept & Measurement of Income, ed. By R. H. Parker & G. C. Harcourt, Cambridge University Press, 1969, pp. 106-119.
5. Economic growth occurs when the social climate is conducive to the appearance of a sufficient flow of New Men. Vigorous economic growth appears when the social climate is appropriate. Flow of New Men (i.e., entrepreneurs) depends on entrepreneurs’ friendly social climate [Higgins, 1978].
6. Professor McClelland’s theory of “Achievement Motivation” modestly suggested that the successful innovative entrepreneurs are those who play key roles in all economic development. McClelland considers analysis of entrepreneurial behaviour in terms of n-achievement to be a considerable refinement of theories analyzing entrepreneurial behaviour in terms of the profit motive alone [Higgins, 1978].
More references
Bebenroth R., & Toshihiro K., Challenges of Human Resource Management in Japan, Routledge Contemporary Japan series, 2011.
Bhaumik M., Code Name God, Penguin Books, 2005.
Chakraborty SK., Values and Ethics for Organizations, Theory and Practice, Oxford University Press, 1998.
Lievens F., & Derek C., Fundamentals of Human Resource Management, The Sage Hand Book of Human Resource Management, 2009
Pattanayak B., Human Resource Management, 04th Edn., PHI Learning Pvt.Ltd.
Prasad LM. Human Resource Management, Sultan Chand & Sons, New Delhi, 2003.
Saha, U. S., Essence of Venture Capital for Software Entrepreneurs for the
development of Software Enterprises in Kolkata, USA, Charleston, SC, 01 April, 2012, ISBN 9781470057275, AMAZON.COM
Saha, U. S., Essence of Management by Value-Added, USA, Charleston, SC, 19 August, 2012, ISBN 9781469999821, AMAZON.COM
Saha, U. S., Essence of Management by Value-Added (MBVA) with an impact
of Value-Adding Multiplier (VAM) in the all-India Manufacturing
sector with a specific focus to the state of West Bengal, Made in
the USA, Charleston, SC, 24 August, 2012, ISBN 9781470061180,
AMAZON.COM
Saha, U. S., EVOLUTION OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
PERSPECTIVES, Copyright © 2012 Dr. Umasankar Saha, All
rights reserved, AMAZON.COM ISBN-13: 978-
1496050106 ISBN-10: 149605010X
Saha, U. S., Challenges and Responses Emerged before the HRM, Copyright © 2015
Dr. Umasankar Saha, All rights reserved, AMAZON.COM, ISBN-13:
978-1508759980.
Articles
Saha, U. S., Accounting For Brand Value-An Emerging Issue, The
Management Accountant, ICWAI, Vol. 33. No. 3, March 1998.
Saha, U. S., Management By Value Added, Research Bulletin, ICWAI, Vol.
xvi, July 1998- Dec 1998.
Saha, U. S., Managing Venture Capital For Software Enterprises – An
Emerging Self-Reliance Strategy For India, Business Studies, The
University Of Kolkata, Vol. xxii, Nos. 1 & 2, January & July 1999.
Saha, U. S., Managing Venture Capital Productivity- An Emerging Issue, The
Management Accountant, ICWAI, Vol. 34. No.12. December
1999.
Saha, U. S., Managing Strategic Development Of Venture Capital For
Entrepreneurship Development- An Emerging Issue, Research
Bulletin, ICWAI, Vol. xviii, July 1999-December 1999.
Saha, U. S., Venture Capital Reforms For It-Software Enterprises, Business
Studies, The University Of Kolkata, Vol. xxiv, Nos. 1 & 2, January
& July 2001.
Saha, U. S., Venture Capital For Brain Capital-Based Entrepreneurs, New
Vistas Of Accounting And Finance, Serampore College,
Department Of Commerce, 2002.
Saha, U. S., Managing Venture Capital For Brain Capital-Based Software
Entrepreneurship- Kolkata’s Self-Reliant Strategy, Sixth
International Accounting Conference, IAA Research Foundation,
January 11-12, 2003.
Saha, U. S., The Road To Reality: Leveraging ITESS Educare For All In The
Discourse Of Diminishing Linguistic And Digital Divide – An
Impact Of Technology And Innovation, Seventh International
Accounting Conference, Hyath Regency, Kolkata, 08th And 09th
January 2005.
Saha, U. S., Is Bengal Shining With The Development Of Women
Entrepreneurship In Knowledge Industry In The Discourse Of
Venture Capital Financing? UGC Sponsored State Level Seminar
Organised And Published By Charuchandra Evening College,
Kolkata, Held On 22-01-2005.
Saha, U. S., Is E-Business Shinning In The Economy Of Bengal? UGC-Asihss
Programme, University Of Kolkata, Seminar Held On: February
25-26, 2006.
Saha, U. S., E-Commerce: A Knowledge-Based Matrix Of The New Business
Paradigm, The Way, Published By Charuchandra Evening College,
Kolkata, 2nd Issue, July, 2006.
Saha, U. S., Venture Capital Financing In Knowledge Based Industry, The
Way, Published By Charuchandra Evening College, Kolkata. 2007.
Saha, U. S., Globalisation: It’s Impact on Managing Quality for All, UGC
Sponsored State Level Seminar Organized and Published by
Charuchandra Evening College, Kolkata. 2008.
Saha, U. S., Managing The Role of Venture Capital in The Development of
Brain Capital-Based Software Entrepreneurship In Kolkata,
Finance India, March 2009 (Vol. xxiii, No. 1. The Quarterly
Journal Of Finance, Indian Institute Of Finance, Ashok Vihar,
Delhi -110052, India.
Saha U., & Saha U.S., “Start-up India” Fostering Entrepreneurship for creating
Employment, paper presented in the National Seminar sponsored
by the UGC organized at Naba Ballygunge Mahavidyalaya, Kol.,
on 28-08-2016